Sorry, your cart is empty :(

How Proper Mesh Tension Transforms Print Quality, Speed, and Consistency — And How Anatol Stretchers Help You Achieve It
In screen printing, few factors influence print quality and production speed as much as screen tension. High, consistent mesh tension ensures fast snap-off, clean ink release, sharp details, and smooth flooding. Low tension, on the other hand, slows production, causes smearing, uneven ink deposits, and leads to rapid stencil and mesh wear.
This guide breaks down why screen tension matters, explains the mechanics behind efficient printing, and provides a step-by-step tutorial on using an Anatol pneumatic screen stretcher — one of the most reliable tools for achieving high-tension, production-ready screens.
Perfect for:
✔ Screen print shops upgrading to higher speed
✔ Printers adopting automatic presses
✔ Shops struggling with smearing, slow peel, or inconsistent ink deposit
✔ Anyone aiming for sharper detail and faster throughput
In printing methods like flexography or lithography, ink transfers from rigid plates at high speed. In screen printing, however, the mesh is flexible — meaning it must move, stretch, and snap back with every stroke.
The pace of this snap-off (also called peel or release) is what ultimately limits print speed.
This is where mesh tension becomes critical.
Low tension (under 25 N) creates several limitations:
Thick or tacky inks — white, metallic, fluorescent, puff — act like glue.
At low tension, the mesh cannot overpower the tackiness fast enough.
Result:
❌ Smeeared prints
❌ Half-moon release pattern
❌ Squeegee outruns the mesh
On automatic presses, every head must wait for the mesh to peel before lifting.
This slows cycle time by 20–50%.
At low tension, the mesh sags under the floodbar, causing:
Low tension forces printers to use:
All of which accelerate wear on squeegees, meshes, and emulsion — adding cost and reducing print quality.
High-tension screens (40–50 N and above) fundamentally improve the entire print process.
✔ Faster mesh snap-off
✔ Sharper details and cleaner edges
✔ More consistent ink distribution
✔ Less stencil wear
✔ Faster production cycles
✔ Reduced operator fatigue
✔ Superior performance with underbases and specialty inks
At around 50 N, many shops report up to 57% increase in hourly output.
At tensions approaching 80–100 N, performance increases even more dramatically.
Anatol pneumatic stretchers are engineered to deliver repeatable, even tension across all frame sizes. Here’s how to use them properly.
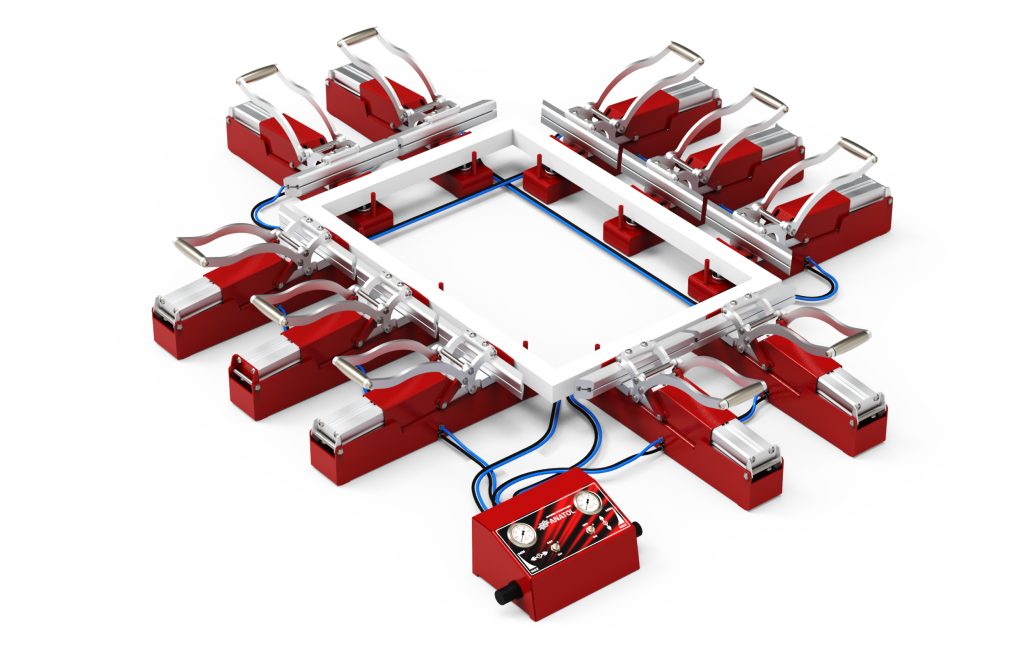
Why this matters:
Stable air pressure = stable tension. Uneven pressure causes uneven stretch.
Why this matters:
Clamp spacing determines force distribution. Uneven spacing causes uneven peel and tension loss during printing.
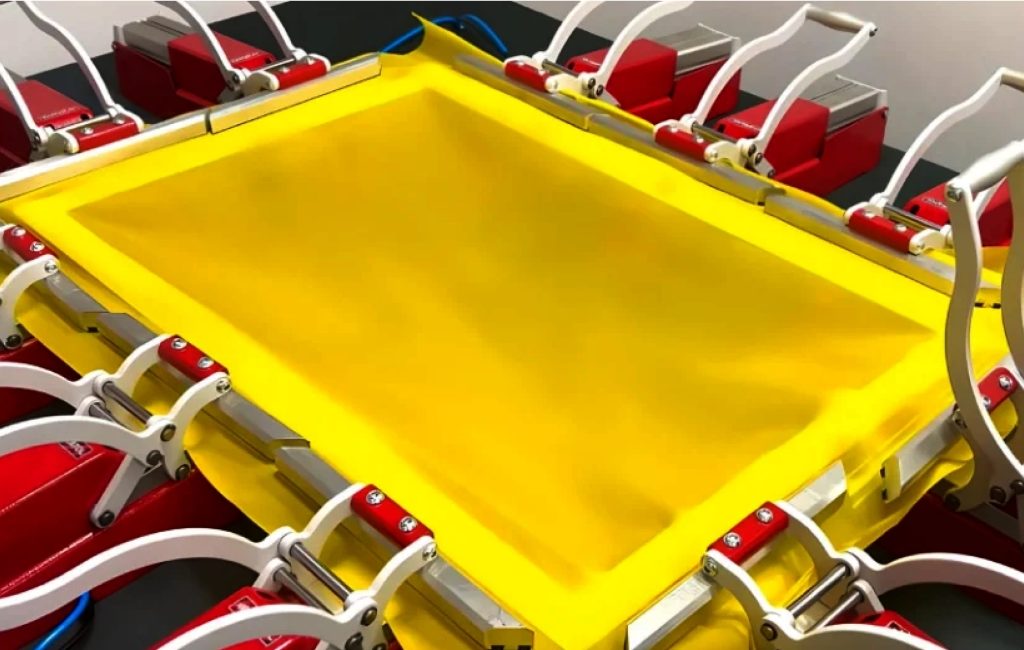
Use the Anatol control box to adjust both mesh directions independently.
Start with:
Why this matters:
Balanced pre-tension prevents distortion and prepares the mesh for high tension without tearing.

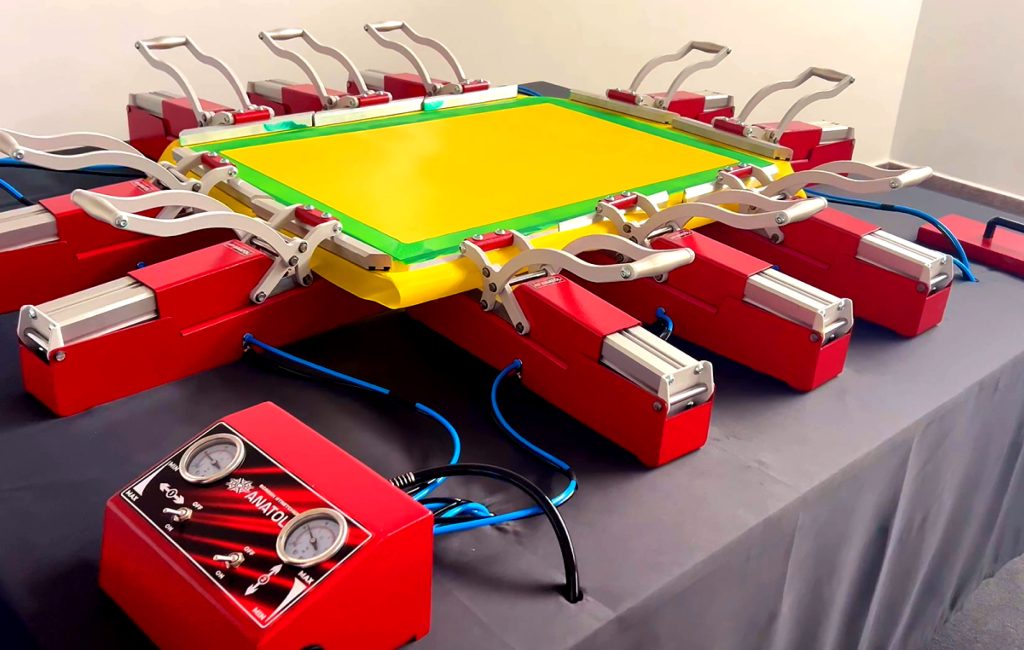
Activate pneumatic pulling.
Watch the tension meter as the mesh tightens.
Recommended stages:
Why this matters:
High tension ensures instantaneous snap-off, consistent flooding, and clean prints even with thick ink deposits.
Mesh naturally relaxes after stretching.
Professional process:
Why this matters:
This creates long-term tension stability — screens won’t lose tension on press.
Secure mesh to frame using glue while clamps remain engaged.
Allow glue to cure fully before releasing pressure.
Why this matters:
If glue cures during tension drop, your screen will instantly lose 2–5 N — enough to affect print speed and quality.

Gradually reduce air pressure to avoid shock relaxation.
Remove clamps carefully.
Use a tension meter to confirm:
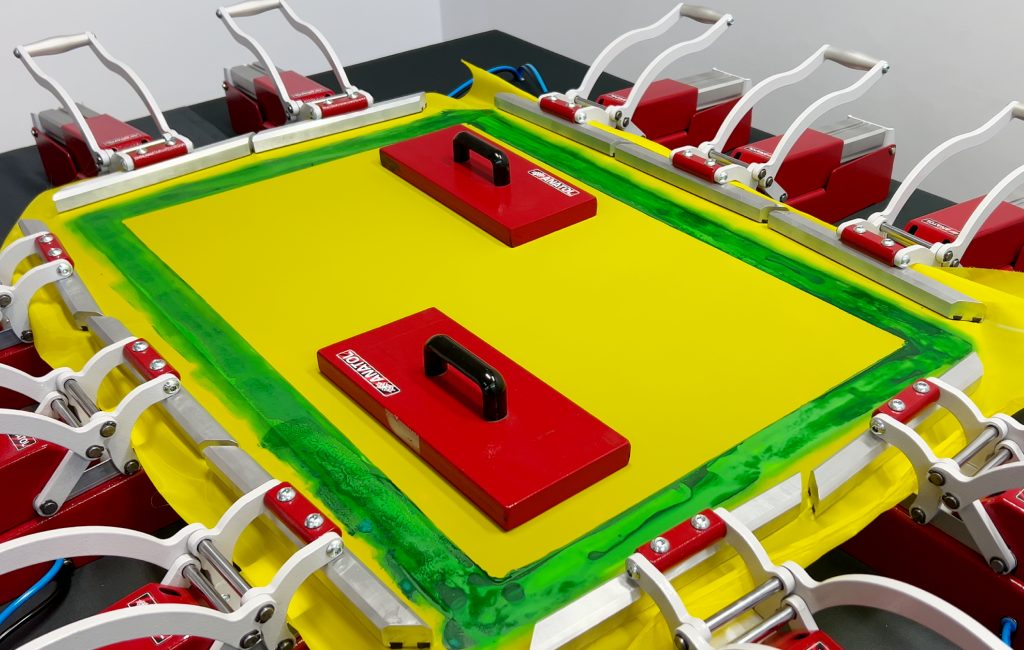
Here’s a video that walks you through the entire stretching process—from positioning the frame and aligning the clamps to reaching and locking in optimal tension—so you can follow along visually as you set up your screens.
Best Practices for High-Tension Printing
✔ Use strong, rigid frames
Aluminum frames handle high-tension better than wooden frames.
✔ Track tension over mesh lifespan
Mesh relaxes after each run. Re-stretching extends screen life.
✔ Use consistent mesh quality
Inferior mesh loses tension quickly.
✔ Train operators
Consistent stretching = consistent printing.
High screen tension is one of the most powerful ways to improve print quality, reduce downtime, and dramatically increase production speed. Anatol’s pneumatic screen stretchers make it easy to achieve and maintain professional-level tension — whether you’re printing underbases, full-fronts, metallics, or high-detail graphics.
By combining proper stretching technique with high-tension best practices and with Anatol’s Screen Stretcher, your shop will see:
Don’t wait—visit the Anatol Screen Stretcher page and submit a Get a Quote request today to streamline your stretching process and boost productivity!
Your message was successfully sent!